Everything You Need to Know About Home Heating Oil
Home heating oil remains an essential energy source for millions of households, particularly in regions with long, cold winters. While alternative heating methods have grown in popularity, home heating oil continues to provide dependable, high-output warmth for residential properties. Understanding how this fuel works, its costs, environmental considerations, and maintenance requirements can help homeowners make informed decisions about their heating systems.
This guide explores the fundamentals of home heating oil, including how systems operate, what influences costs, how to maintain efficiency, and where the industry is headed. Whether you currently rely on oil-based heating or are evaluating your options, having a clear understanding of this fuel source is key to managing comfort, expenses, and long-term performance.
What Is Home Heating Oil?
Understanding the Basics
Home heating oil is a refined petroleum product used in furnaces and boilers to heat residential buildings. It is most commonly found in colder regions where access to natural gas infrastructure may be limited. Heating oil systems are valued for their ability to produce high levels of heat quickly, making home heating oil well suited for extreme winter conditions.
Derived from crude oil through a refining process, this fuel is similar to diesel but formulated specifically for residential use. Despite shifts toward electric and renewable heating technologies, home heating oil remains a practical and reliable solution for many homeowners.
Types of Heating Oil
The most widely used residential fuel is Number 2 heating oil, known for its balance of efficiency and affordability. Kerosene is another option, typically used in colder climates because it resists gelling at low temperatures. In recent years, Bioheat fuel has gained attention as a blend of traditional heating oil and biodiesel, offering reduced emissions while still functioning within standard home heating oil systems.
Each type of fuel serves different needs depending on climate, system compatibility, and environmental priorities. Availability often varies by region.
History and Evolution
Home heating oil became popular in the early 20th century as households transitioned away from coal. Advancements in refining and burner technology improved efficiency and cleanliness over time. During the 1970s oil crisis, interest in alternative energy sources increased, leading to diversification within the residential heating market.
Today, continued innovation has produced cleaner-burning fuels and more efficient equipment, allowing home heating oil to remain relevant despite growing competition from renewable energy sources.
Comparison With Other Fuels
Compared to natural gas, electric heat, and propane, home heating oil delivers a high heat output per unit of fuel. Natural gas can be more cost-effective where infrastructure exists, while electric heating offers lower on-site emissions but may struggle in extreme cold. Propane provides flexibility but often comes with higher fuel costs.
For homeowners prioritizing reliability during harsh winters, home heating oil continues to be a dependable option.
How Home Heating Oil Systems Work
System Components
A typical system includes a storage tank, oil burner, heat exchanger, and distribution system. The tank stores fuel, which is delivered to the burner as needed. The burner ignites the fuel, producing heat that warms air or water, which is then circulated throughout the home.
Thermostats regulate operation by signaling when heat is required, helping maintain comfortable indoor temperatures while conserving home heating oil usage.
The Role of the Oil Burner
The oil burner is the core of the system. It atomizes the fuel into fine droplets, mixes it with air, and ignites the mixture to create a controlled flame. This heat transfers through the exchanger and into the home’s distribution system.
According to InEnergy, modern burners typically operate at efficiency levels between 85% and 92%, allowing homeowners to get maximum performance from their home heating oil supply.
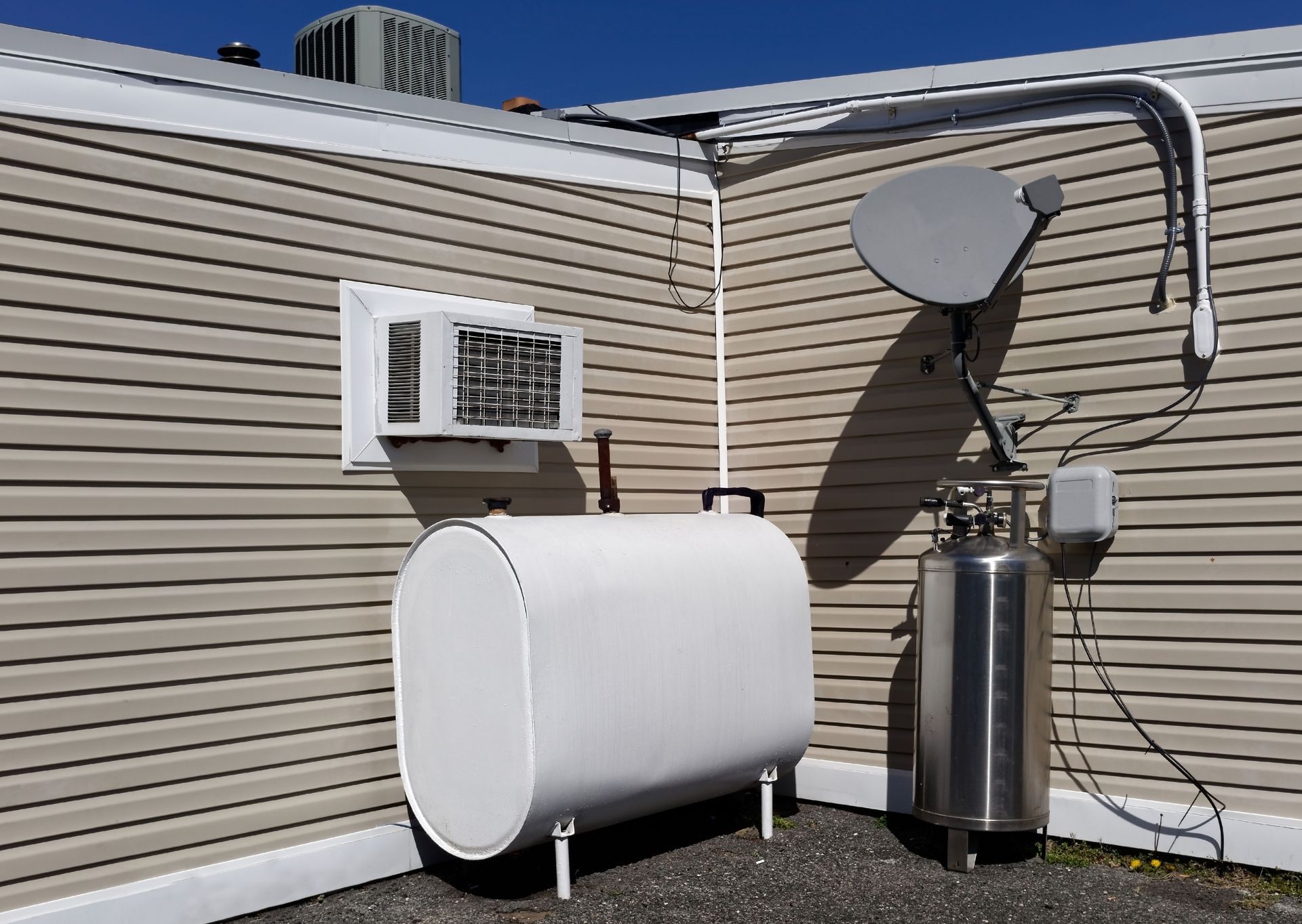
Storage and Safety
Heating oil tanks are commonly made of steel or fiberglass and can be installed indoors or outdoors. Routine inspections help prevent leaks, corrosion, or structural damage. Proper placement and adherence to safety regulations reduce fire and environmental risks.
Monitoring tank condition and fuel levels helps homeowners avoid interruptions and safely manage their home heating oil supply.
Delivery Methods
Fuel is delivered by local suppliers either on a scheduled basis or upon request. Many companies now use automated monitoring systems that track tank levels and schedule deliveries automatically. These services help prevent run-outs and improve convenience.
Some suppliers also offer pricing plans designed to stabilize home heating oil costs throughout the year.
Costs and Budgeting for Home Heating Oil
Seasonal Price Fluctuations
Prices generally rise during fall and winter when demand peaks. Many homeowners choose to purchase fuel during warmer months through pre-buy or fixed-price contracts to secure lower rates.
Monitoring seasonal trends can help reduce overall home heating oil costs.
Cost-Saving Strategies
Improving insulation, sealing drafts, and using programmable thermostats can significantly reduce fuel consumption. Regular system maintenance also improves efficiency and prevents waste. Some homeowners supplement oil systems with space heaters to reduce usage in low-traffic areas.
Small efficiency improvements can lead to meaningful reductions in home heating oil consumption over time.
Payment Plans and Assistance
Many suppliers offer budget plans that spread heating costs evenly across the year. Fixed-rate contracts provide price stability, while pay-as-you-go options offer flexibility.
For qualifying households, assistance programs can help offset the cost of home heating oil during peak winter months.
Environmental Impact and Considerations
Carbon Emissions
Burning heating oil releases carbon dioxide and other emissions, contributing to climate change. However, modern fuels and systems produce significantly fewer emissions than earlier generations. Improved efficiency means less fuel is required to achieve the same heating output.
Cleaner blends and efficient equipment continue to reduce the environmental footprint of home heating oil.
Technological Improvements
Ultra-low sulfur fuels have lowered sulfur emissions, improving air quality. High-efficiency boilers and burners now capture more usable heat, reducing waste and fuel usage.
Regulations and Standards
Stricter regulations govern fuel composition, emissions, and equipment performance. Compliance has encouraged innovation and cleaner heating practices. Incentives and rebates often support upgrades to more efficient systems.
Renewable Alternatives
Bioheat, heat pumps, and solar thermal systems offer alternatives or supplements to traditional heating methods. While some options require higher upfront investment, they can reduce long-term emissions and operating costs depending on location and system compatibility.
Maintenance and Efficiency Tips
Routine Maintenance
Annual maintenance keeps heating systems operating safely and efficiently. Inspections typically include cleaning burners, replacing filters, and checking fuel lines. Regular servicing extends equipment lifespan and prevents unexpected breakdowns.
System Upgrades
Upgrading to newer equipment often results in improved efficiency, quieter operation, and better temperature control. Long-term fuel savings can offset the initial investment.
Warning Signs
Unusual noises, inconsistent heating, increased fuel usage, or visible soot may indicate system issues. Addressing these signs early protects both comfort and home heating oil efficiency.
Future Trends in Home Heating Oil
Advancing Technology
Smart burners, remote monitoring, and internet-connected controls are shaping the future of oil-based heating. These technologies allow for more precise control and early detection of performance issues.
Efficiency Innovations
Condensing boilers and advanced heat exchangers continue to improve energy utilization, allowing modern systems to extract more heat from each gallon of home heating oil.
Renewable Integration
The integration of biodiesel into heating fuel reflects a gradual shift toward renewable energy. Blended fuels provide a practical step toward sustainability without requiring system replacement.
What This Means for Homeowners
Homeowners can expect continued improvements in efficiency, cleaner fuels, and smarter system management. Staying informed helps protect long-term comfort and heating budgets.
Conclusion
Home heating oil continues to serve as a reliable and effective heating solution for millions of households. Its high heat output, improving efficiency, and adaptability through cleaner fuels make it a viable option despite a changing energy landscape.
By understanding system operation, managing costs, maintaining equipment, and staying aware of future developments, homeowners can make the most of their home heating oil investment for years to come. If you need home heating oil, contact Frederick Brothers Oil & Propane.





Share On: